Let’s Talk About Tooth Sensitivity!
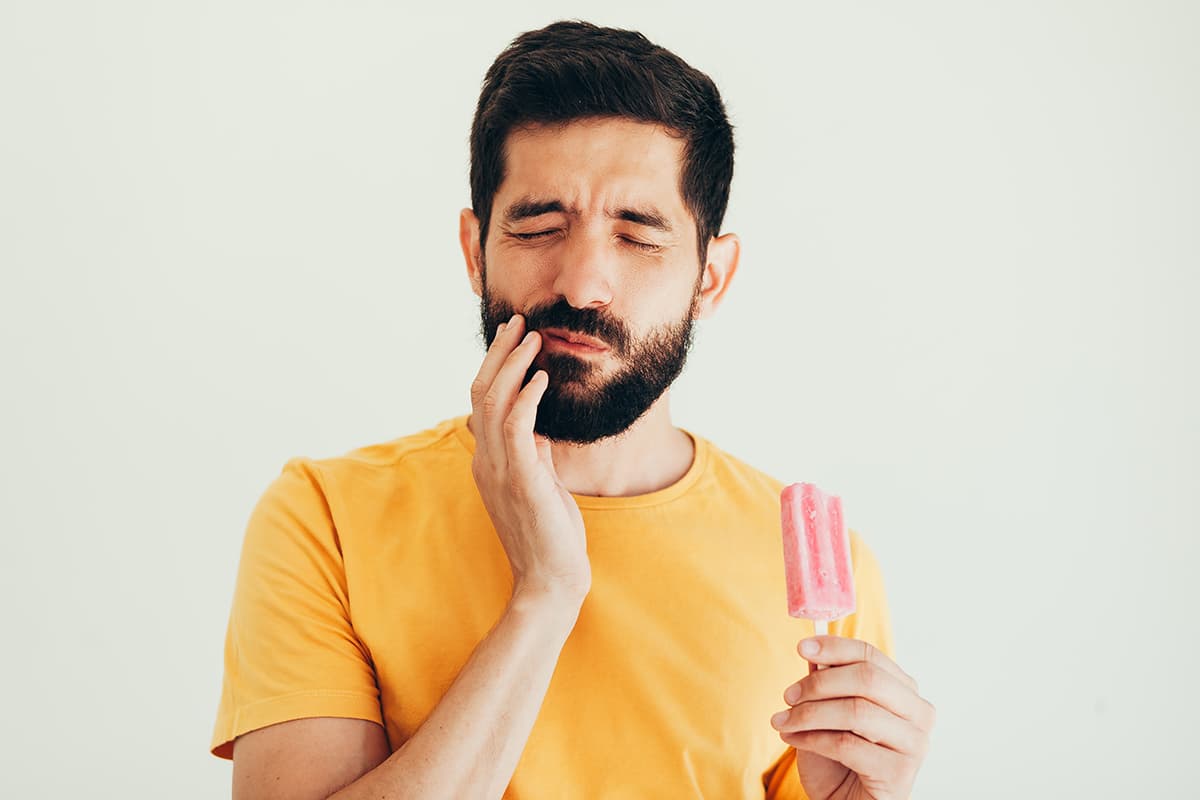
Tooth sensitivity is one of the most common complaints that dental professionals hear from their patients. According to studies, tooth sensitivity affects over 12% of adults and over 33% of adults have untreated decay. Although enamel erosion and untreated decay can be a common reason for sensitivity, many other reasons for tooth pain & sensitivity also exist.
While sometimes, sensitivity requires professional dental treatment in the office, some types of sensitivity can be reduced with some simple homecare modifications.
The first step in reducing your tooth sensitivity is understanding its causes and symptoms so you can begin to find relief for your sensitivity.
So, let’s talk about sensitive teeth, shall we?
What Causes Sensitivity?
Tooth and gum sensitivity can be caused by the following reasons:
- Enamel erosion: Also called dentin hypersensitivity happens when the enamel is exposed to wear and tear by acids or mechanical forces, which can thin enamel and expose the next & more sensitive tooth layer called dentin.
- Tooth decay: Commonly referred to as cavities, tooth decay is a softening of the tooth enamel that leads to holes in the tooth in which bacteria can infect.
- Infected tooth nerve: If decay is left untreated, bacteria can infect the dental pulp, which is the nerve of the tooth. The nerve becomes infected and can cause pain that must be treated with a root canal.
- Tooth or filling crack: Even small unseen cracks in teeth or fillings can cause sensitivity.
- Recent dental procedures: Having recent dental procedures can temporarily stimulate the tooth nerve, which can cause sensitivity for a few weeks following the procedure.
- Tooth whitening: Ingredients in common tooth whitening products can cause temporary tooth sensitivity.
- Gum recession: If gums recede, they are unable to protect the roots of the teeth, which can result in root sensitivity. Also, if gums recede, bacteria that cause gum infection can rest at the gum line and cause gum sensitivity.
- Gum infection: Gum infections such as gingivitis and periodontal disease can be the source of gum sensitivity.
- Bite Issues – Grinding or clenching: Forces that are created by grinding, clenching, or an unbalanced way that our teeth align can cause stresses to your teeth and oral tissues that lead to tooth and gum sensitivity.
- Sinus infection: Because the roots of upper teeth are close to our sinuses, when sinuses are infected, they can become inflamed and put pressure on tooth roots, which can cause teeth to feel achy or painful.
What are the Symptoms of Tooth & Gum Sensitivity?
When you feel sensitivity in your mouth, the first thing to determine is if your sensitivity is coming from your tooth or gums.
Tooth Sensitivity
If your sensitivity is coming from a tooth, the next step is to determine if your tooth is sensitive to hot, cold, or sweets because each time of sensitivity can have a different meaning. Are you sensitive to?
- Hot?
- Cold?
- Sweets?
- Intermittent Dull Ache?
- Sharp or Throbbing Pain?
The type of sensitivity that you have can indicate different problems. For example, hot sensitivity can indicate problems with the nerve of your tooth. Cold sensitivity can indicate exposed root surfaces, worn enamel, or even a cracked filling or tooth. Sweet sensitivity can indicate that you have tooth decay (a cavity).
A dull ache and sharp or throbbing pain may indicate an infection within the tooth or possibly a sinus infection.
Although these symptoms and problems are common, they are not always the same and may need different treatment for relief.
Gum Sensitivity
Gum disease affects half of American adults!
If your gums are the culprit of your sensitivity, try to check the area. Do you see or feel?
- Bleeding?
- Redness?
- Swelling?
- Gums Pulled Away from Teeth?
- Intermittent Gum Ache?
If gums appear pulling away from your teeth, that can indicate gum recession that may require professional treatment.
Gum sensitivity & the above symptoms can be signs of an early gum irritation or even a more severe gum infection. Failure to identify and treat gum infections can lead to infections of the jawbone that can become painful, cause harm to your overall health, and cause tooth loss.
Can Tooth Sensitivity Be Treated at Home?
Sometimes, tooth sensitivity, particularly cold sensitivity that is caused by enamel erosion or gum recession can be alleviated at home. Mild gum irritations can often be treated at home with simple homecare modifications. Some common home remedies include:
- Sensitivity Toothpaste: Over-the-counter toothpaste for sensitivity block the tubules that send sensations to the tooth nerve. If sensitivity is caused by enamel erosion, these kinds of toothpaste may be effective
- Homecare Modifications: Modifications such as using only a soft toothbrush may reduce dentin hypersensitivity. Increased homecare such as flossing, water flossers, or antibacterial mouth rinses may reduce bacteria that cause mild gingivitis.
- Dietary Modifications: Avoiding highly acidic foods can help to reduce tooth sensitivity.
When Should I Call My Dentist?
While having sensitive teeth is not usually considered a dental emergency, teeth that are causing you prolonged sensitivity should be examined by a dentist to diagnose the causes or rule out some of the more serious causes mentioned here and offer treatment and advice.
If at-home remedies do not alleviate sensitivity or sensitivity increases, you should call your dentist for an appointment to evaluate the problem. Your dentist can examine your mouth to determine if you have a tooth or gum infection and provide appropriate treatment.
Keep in mind that sensitivity is not the same as pain. If you experience dental pain for longer than 48 hours, you should contact your dentist immediately as it may be the sign of a serious infection that could affect your overall health.
As your dental professionals, we are here to answer your questions and help you find the best ways to alleviate your dental sensitivity!